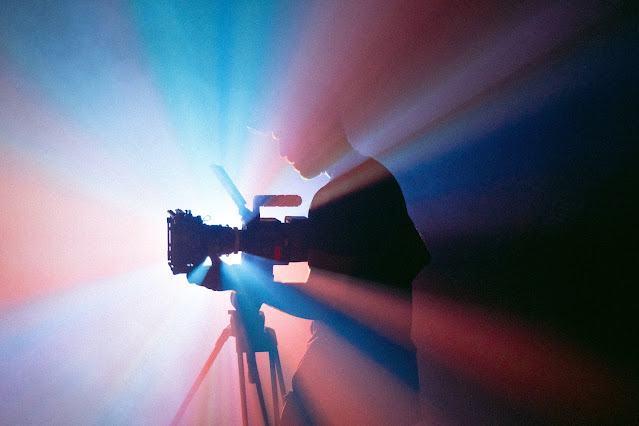
Cinematography is an art form that combines technical expertise, visual storytelling, and creative vision to bring stories to life on the screen. Whether it's capturing breathtaking landscapes, intimate character moments, or high-octane action sequences, cinematographers rely on a set of fundamental principles to create visually stunning and impactful imagery. In this blog, we will delve into the three basics of cinematography—lighting, composition, and camera movement—and explore their significance in crafting compelling visuals.
Lighting
Lighting is one of the most critical elements in cinematography, as it sets the mood, enhances the atmosphere, and directs the viewer's attention. Cinematographers harness the power of light to shape the scene and evoke specific emotions. This section will delve into various aspects of lighting, including:
1. Natural and Artificial Light: Understanding the qualities and characteristics of both natural and artificial light sources and how they can be utilized to create desired effects. Exp[lore more about the natural Lighting
2. Lighting Techniques: Exploring techniques such as three-point lighting, high-key lighting, low-key lighting, and chiaroscuro to achieve specific lighting setups and enhance the visual impact.
3. Color Temperature: Discussing the importance of color temperature in setting the tone and mood of a scene and how cinematographers use techniques like color grading to manipulate colors and create a cohesive visual aesthetic.
Composition
Composition refers to the arrangement of visual elements within the frame of a shot. It plays a crucial role in guiding the viewer's attention, conveying meaning, and creating visually pleasing images. This section will explore various aspects of composition, including:
1. Rule of Thirds: Discussing the rule of thirds and how cinematographers use it as a guideline to create balanced and visually appealing compositions.
2. Framing and Depth: Exploring techniques such as leading lines, foreground/background elements, and depth of field to add depth and dimension to shots.
3. Aspect Ratios: Discussing the different aspect ratios and their impact on storytelling and visual aesthetics.
Camera Movement :
Camera movement adds dynamism, perspective, and emphasis to the visual narrative. It allows cinematographers to create immersive experiences, highlight key elements, and evoke specific emotions. This section will delve into various camera movements, including:
1. Pan and Tilt: Exploring the use of horizontal and vertical camera movements to scan the scene, follow action, or reveal information.
2. Tracking and Dolly Shots: Discussing the use of tracking shots and dolly movements to add fluidity and convey a sense of movement.
3. Handheld and Steadicam: Exploring the handheld camera technique and the use of stabilizing devices like steadicams to create a sense of immediacy or simulate the point of view of a character.
Conclusion:
Mastering the three basics of cinematography—lighting, composition, and camera movement—is essential for aspiring cinematographers. These fundamentals form the foundation of visually captivating storytelling and are crucial in creating memorable and impactful cinematic experiences. By understanding the principles and techniques associated with each of these basics, cinematographers can effectively communicate the intended emotions, guide the viewer's attention, and enhance the overall visual aesthetics of their projects.
Aspiring cinematographers should continually study and practice these fundamentals, experimenting with different lighting setups, compositional techniques, and camera movements to develop their own unique visual style. Through a deep understanding and mastery of the three basics of cinematography, aspiring cinematographers can elevate their craft and bring their artistic vision to life on the screen.